1. How does a motherboard work?
How Does a Motherboard Work? An In-Depth Look
 The motherboard is the main circuit board inside a computer. It connects all the computer’s parts and allows them to communicate with each other. Here’s how it works in simple terms.
The motherboard is the main circuit board inside a computer. It connects all the computer’s parts and allows them to communicate with each other. Here’s how it works in simple terms.
It is like the heart of a computer. It holds the CPU, RAM and other essential parts. Without it, your computer wouldn’t work.
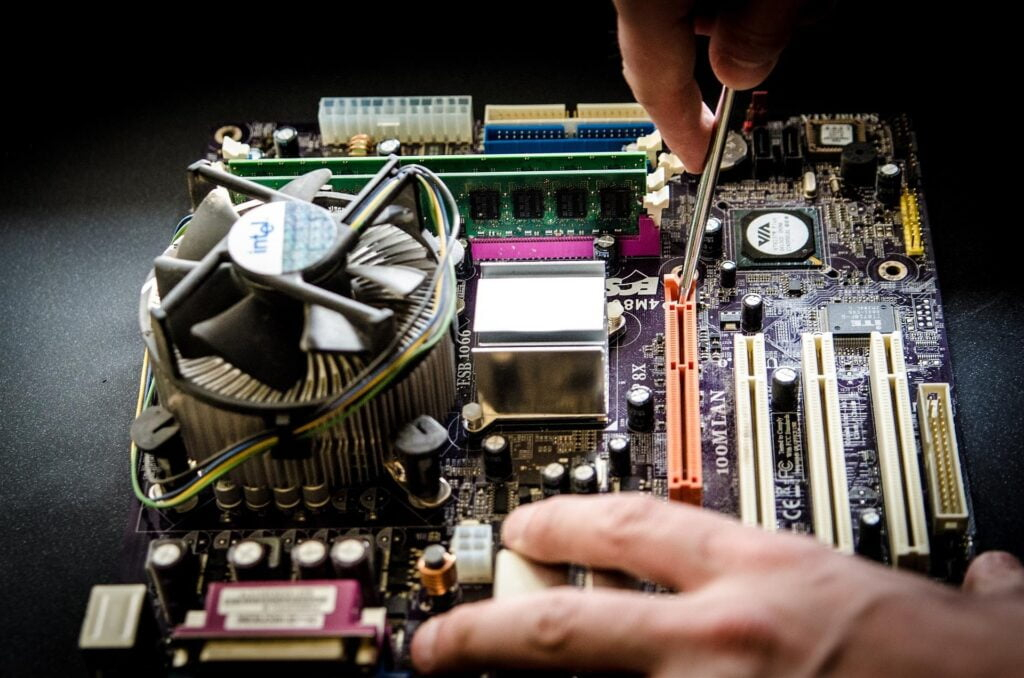
Main Components of the Motherboard
CPU Socket: This is where the CPU (Central Processing Unit) goes. The CPU is the brain of the computer. It processes instructions and performs calculations.
RAM Slots: These slots hold the RAM (Random Access Memory) sticks. RAM is like the short-term memory of the computer, storing data that the CPU needs quickly.
Chipset: The chipset controls data flow between the CPU, memory, and other parts. It’s divided into the Northbridge and South bridge.
BIOS/UEFI Chip: This chip contains firmware that initializes hardware during the startup process. It’s essential for booting up the computer.
Expansion Slots: These slots allow you to add extra components like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards.
Power Connectors: These connectors supply power to the motherboard and other components.
Storage Connectors: These are used to connect storage devices like hard drives and SSDs.
Input/Output Ports: These ports connect external devices like keyboards, mice, and monitors.
These all things are connected with the this.
How Does It All Work Together?
 When you press the power button, electricity flows through the motherboard. The BIOS/UEFI chip initialize the hardware and performs a Power-On Self-Test to check if everything is working correctly.
When you press the power button, electricity flows through the motherboard. The BIOS/UEFI chip initialize the hardware and performs a Power-On Self-Test to check if everything is working correctly.
The CPU then takes over, reading instructions from the RAM and executing them. Data flows through the chipset, which ensures that everything is communicated correctly.
Data Flow on the Motherboard
Data travels along pathways called buses. There are different types of buses for different types of data:
System Bus: Connects the CPU to the RAM and chipset.
Data Bus: Transfers actual data between components.
Address Bus: Carries memory addresses.
Control Bus: Carries control signals.
What is the Role of the Chipset?
The chipset acts as a traffic controller. The Northbridge handles communication between the CPU, RAM, and graphics card. The South bridge manages communication with the rest of the computer, like storage devices and peripheral ports.
How to Expand and Upgrade it?
 You can’t expand a motherboard but you can expand other components of it. Motherboards have expansion slots for upgrading your computer. You can add more RAM, a better graphics card, or additional storage. This makes your computer more powerful and capable of handling more tasks.
You can’t expand a motherboard but you can expand other components of it. Motherboards have expansion slots for upgrading your computer. You can add more RAM, a better graphics card, or additional storage. This makes your computer more powerful and capable of handling more tasks.
Cooling the Motherboard
Computers generate heat, and the motherboard needs to stay cool. It has heatsinks and sometimes even small fans to dissipate heat. Proper cooling ensures the computer runs smoothly and lasts longer.
Types of Motherboards
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended): The most common type, used in desktop computers.
MicroATX: Smaller than ATX, used in smaller computers. It’s easy to carry somewhere.
Mini-ITX: Even smaller, in compact or specialised computers.
How to Maintain it?
You have to clean it at least once a week. Dust can cause overheating. Use compressed air to clean the motherboard. After that ensure all the cables are properly connected.
Troubleshooting Common Issues!
No Power: Check the power supply and connections.
No Display: Ensure the monitor is connected correctly and the graphics card is seated properly.
Random Crashes: This could be due to overheating or faulty RAM. Check the cooling system and test the RAM.
 The motherboard is a part of the computer, connecting all the components and ensuring they work together. Understanding how it works helps in maintaining and upgrading your computer. Keeping the motherboard clean, ensuring proper cooling, and updating the BIOS/UEFI are essential for a well-functioning computer.
The motherboard is a part of the computer, connecting all the components and ensuring they work together. Understanding how it works helps in maintaining and upgrading your computer. Keeping the motherboard clean, ensuring proper cooling, and updating the BIOS/UEFI are essential for a well-functioning computer.
By knowing the basics of the motherboard, you can troubleshoot issues, perform upgrades, and keep your computer running efficiently. It’s the backbone of your computer, supporting everything you do on it.